‘Spondyloarthritis’ is a general term for a group of inflammatory conditions that primarily affect the joints of the spine.
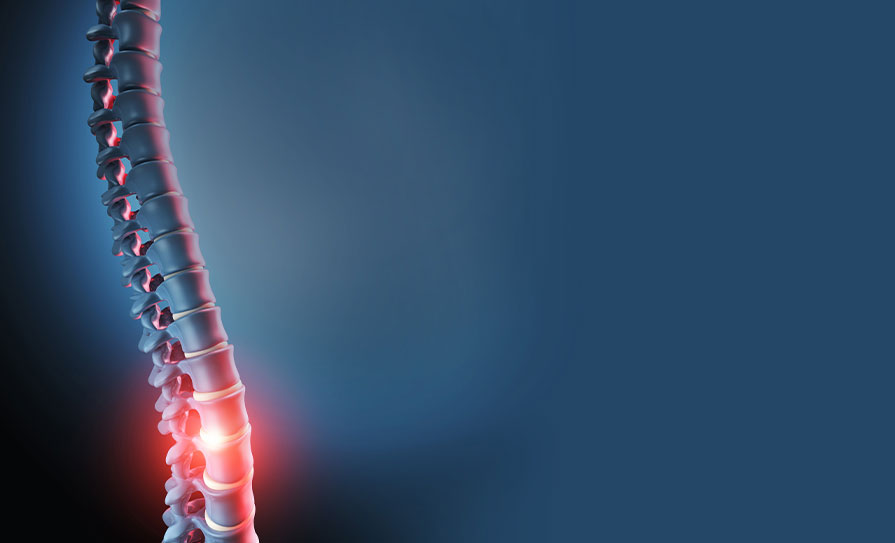
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS), the most common of these conditions, is a painful, progressive, long-term disease where the main symptoms are pain and stiffness in the sacroiliac joints in the lower back. Whilst the affected areas are primarily in the spine, any area of the body where ligaments attach to bone can be similarly affected.
The condition can affect people in different ways, from mild discomfort to severe debilitating pain that can have a huge impact on daily living.
In this article, we will give a comprehensive overview of the condition, looking at symptoms, causes and then diagnosis and treatment, along with self-help and advice to help people help themselves to manage their condition for maximum improvement.
In terms of prevalence, whilst only a few studies have been done, it is generally accepted that the figures for those living with the condition globally range from 0.1-to-1.4 per cent of population. In Ireland, between 0.1-to-0.2 per cent have AS.
Whilst AS can affect anyone at any time of life, onset of AS is usually in the 20s, with a gender balance of 2:1 male-to-female, so, is most common in younger men.
WHAT IS ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS?
If we look at the etymology of the phrase, this helps us understand in a very basic way what the disease does. Ankylosis is the ‘fusing together’ or uniting of bones. Spondylitis – from the Greek spondylos for vertebrae, gives us the first part, with the suffix ‘itis’ indicating inf lammation. Note that spondylitis should not be confused with the more common condition spondylosis — age-related wear and tear on the joints in the spine.
With AS, inf lammation, usually originating in sacroiliac joints at the base of the spine, leads to a reaction from the body that puts down bone (calcium) between the vertebrae, replacing the elastic ligament tissue. It is this bony overgrowth that leads to a reduction in f lexibility in the spine as the bone continues to grow at the sides of the vertebrae. Over time, this causes the bones to fuse together, which creates stiffness and pain and in severe cases, can result in permanent rigidity and curvature of the spine. In addition, the condition can spread to other parts of the body.
SYMPTOMS
Commonly starting in the 20s, the onset of symptoms of AS is usually a slow and gradual process, developing over months or maybe years. The main symptoms are:
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back (sacroiliac joints), usually first thing in the morning lasting more than 30 minutes, which then eases as the day progresses or after activity such as stretching. These symptoms may ebb and flow over time, however, as they develop, the pain may still ease with exercise, but may become more constant when at rest.
- Pain in the buttocks and backs of the thighs, which becomes progressively worse over weeks and months.
- Constant tiredness and general fatigue.
The symptoms above are indicative of classic AS in the lower spine, however other parts of the body can also be affected by the disease.
ARTHRITIS
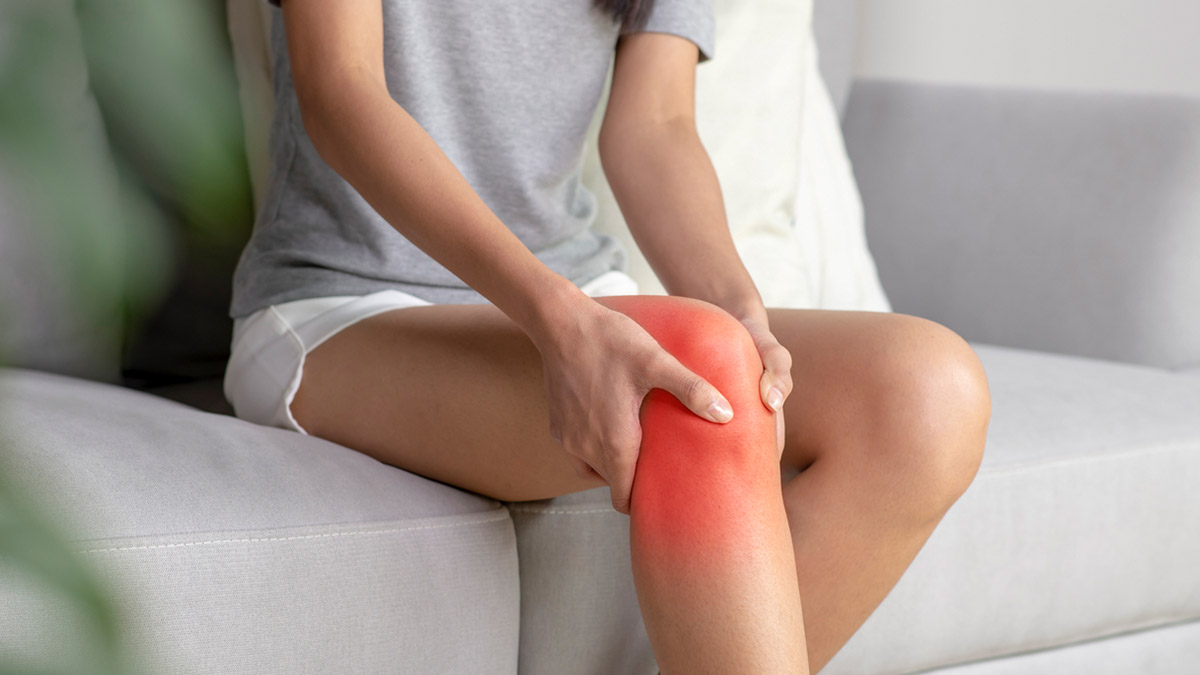
AS may cause other arthritic-type symptoms in other joints in the body and would show as:
- Warmth and swelling in the affected joint (knee for example).
- Pain in the affected joint when moving which does not ease with exercise.
- Tenderness to touch when examined.
AS may also precipitate another condition called enthesitis, which is inflammation caused by AS at any other site in the body where a tendon or ligament attaches to bone.
Most common examples are:
Behind or under the heel — painful inflammation where the Achilles tendon joins the heel bone or in the tendon in the arch of the foot may make it uncomfortable to stand on hard surfaces, which may require custom-made orthotics to help alleviate pain.
Chest pain — If AS is affecting your upper (thoracic) spine, this will result in gradual feeling of constriction in the chest due to reducing movement and elasticity in ribs and sternum. This can affect breathing, making it difficult to inhale deeply and fill the lungs fully or cause a shortness of breath following light activity.
Iris inflammation (iritis) in the eye can be another complication of AS. It is thought that up to 40 per cent of people with AS may develop an eye problem. With this condition, the eyes become painful showing red, bloodshot, and watery symptoms with an associated sensitivity to light sometimes accompanied by blurred vision. If this occurs, especially if there is diminished vision, it’s vitally important to seek immediate medical help via your GP or optician or in emergency, the emergency department. The condition is usually successfully treated with corticosteroid eye drops.
CAUSES
Similar to other forms of arthritis, ie, rheumatoid arthritis, the cause of AS is not known. There is some evidence of a link to a gene HLA-B27. Studies have shown that 90 per cent of people with AS carry the gene and that it can be passed from parent to child. A blood test can show if an individual carries the gene, something that is considered when diagnosing possible AS. For someone with AS carrying HLA-B27, the chances of passing the gene to their children in 50 per cent and even then, only between 5-to-20 per cent of children who inherit the gene will develop AS in later life. So, if a person carries the HLA-B27 gene, they will not automatically develop AS. Figures show that around 8 per cent of general population carry the gene and the vast majority do not have AS.
It is thought that up to 40 per cent of people with AS may develop an eye problem
As mentioned, a blood test can indicate if the gene is present but in isolation, is not that reliable as many have the gene, but not AS. A positive indication combined with a range of other diagnosed factors would give a more accurate assessment.
There are some suggestions that environmental factors may trigger AS, however, what these may be is unknown.
Bowel disease (IBD) may be a contributing factor in the development of AS and there is current research in progress that suggests that as IBD and AS share some similar genetic characteristics; so much so that a specific treatment for IBD (rifaximin) may also contribute to an easing of symptoms and development of AS. It is early days regarding research on use of rifaximin for AS, but initial results look encouraging.
DIAGNOSIS
Back pain is the most commonly reported chronic condition in Ireland; because of this, AS often starts off as what most people think is just back pain. As is also commonly the case, people in Ireland put up with a certain amount of back pain, not wanting to ‘bother the doctor’ and will use OTC solutions and rest to alleviate and manage symptoms.
It is only when the pain becomes more constant, for example when resting, that people may present to the GP with the issue. From the GP perspective, AS can be notoriously difficult to diagnose straight away, so they will dig into the symptoms to establish:
- The exact nature of the symptoms — do they come and go? Are they constant?
- Do they improve with rest? Do they cause interrupted sleep?
- Are there other parts of the body affected?
Once the full extent of the symptoms has been identified, the doctor may order further blood tests to establish if there is inflammation present in the spine and/ or joints.
Based on these outcomes then, if the GP suspects AS is the cause, they may refer the patient to a consultant rheumatologist for further investigation.
It is likely that the rheumatologist will initiate imaging tests such as x-ray, MRI, or ultrasound to gain further insight into the condition of the affected joints. In the early stages of AS development, little may show on x-ray — however, MRI may offer a better outcome in terms of guiding information.
In addition, the rheumatologist may also have a further blood test undertaken to establish if the HLA-B27 gene discussed earlier is present.
With so many variables at play, diagnosis of AS, even with all the diagnostic jigsaw pieces present, can still be difficult and can take a long time, with some patients waiting years in some cases to get confirmation of AS.
A confirmed diagnosis can usually be given if imaging shows inflammation in the sacroiliac joints (sacroiliitis) or without sacroiliitis, with more than one of the following:
- Lower back pain with duration of more than 12 weeks that improves with exercise but does not get any better with rest.
- Limited or decreasing levels of mobility in the lower back.
- Limited chest expansion for your age/ gender profile.
Once diagnosis has been established, then a more condition-specific treatment regimen can be instigated.
TREATMENT
There is no cure for AS, however, with a range of treatment options, used together, living with the condition and maintaining a decent quality of life can be achieved.
Combination treatments focus on three areas:
- Medication.
- Physiotherapy.
- Exercise.
- Medication
- Analgesics
PARACETAMOL
- Paracetamol is the initial choice for many, especially in the early stages or perhaps prior to a proper diagnosis of the condition.
- Widely available, available without prescription, paracetamol can be taken regularly.
- Side effects are rare.
- Can be taken as a pre-emptive assist prior to activity or exercise to help keep pain to a minimum.
- May be only option for some if NSAIDs are contraindicated.
CODEINE
- Can be used with paracetamol (co-codamol) if stronger pain management is required.
- Available in other combinations (aspirin, ibuprofen) over the counter.
- Caution should be used, as codeine carries an increased risk of side-effects:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Constipation.
- Drowsiness.
- Again, could be best option if NSAIDs are an issue.
- Patients should review use regularly with pharmacist to avoid potential dependency problems.
NSAIDS
- With both pain management and anti-inflammatory properties, NSAIDs may be a more effective choice for those with AS than other analgesics.
- NSAIDs are available as capsules, tablets, suppositories, creams, gels, and injections, so may be more accessible for a wider range of patients.
- Key is trying to find one that works best for the individual — achieves best result at lowest dose in the least time.
- Available both over the counter and by prescription. Most popular examples are:
- Ibuprofen.
- Diclofenac.
- Naproxen.
- Celecoxib.
- Etoricoxib.
- Can cause a range of side-effects, particularly stomach-related, such as:
- Diarrhoea.
- Upset stomach.
- Nausea.
- Indigestion.
- Potential damage to the stomach lining.
Over-use can be associated with serious bleeding. For this reason, you must not use NSAIDs with aspirin. If you have asthma, there is a risk of it becoming worse when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs be unsuitable for patients taking other medications such as anticoagulants, SSRIs, hypertensive medication.
In a small number of people, NSAIDs can cause heart problems, ie, diclofenac and COX-2 inhibitors. The European medicines watchdog issued a warning in July 2013 stating that diclofenac can significantly increase the risk of heart problems such as heart attack and stroke in those already at risk of these problems.
COX-2 inhibitors are a type of NSAID that directly targets cyclooxygenase-2, COX-2. Examples include celecoxib and etoricoxib. They demonstrate a significantly reduced risk for upper and lower gastrointestinal complications compared with conventional NSAIDs. However, evidence suggests that some of these agents, at some doses, may be associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular adverse events compared with no therapy. COX-2 inhibitors are best avoided in patients with cardiovascular issues.
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENTS
If a patient’s condition cannot be managed or controlled using NSAIDs or analgesics, anti-TNF medication may offer a solution.
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is produced by cells when tissue becomes inflamed. This is a newer approach to managing AS-related pain. There is some evidence from the successful use of anti-TNFs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, which is providing good information regarding the impact of long-term use.
Administered through SC injection, which with training the patient can do for themselves, anti-TNFs are usually prescribed by a rheumatologist. The decision to prescribe anti-TNFs is usually made following careful consideration and consultation as to their potential effectiveness on a case-by-case basis. The drug can also be given as a tablet to help alleviate pain in swollen joints.
Once prescribed, the response to the
treatment is closely and regularly monitored — if there is no significant improvement after three months, treatment will cease.
Biological treatments include TNF-alpha inhibitors (etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and certolizumab), rituximab and tocilizumab.
Side-effects from biological treatments are usually mild and include skin reactions at the site of injection, infections, nausea, fever, and headaches. They should be used in caution in patients who have had tuberculosis (TB), septicaemia and hepatitis B in the past. There is a slight risk that biological treatments can reactivate these conditions and, in rare cases, trigger new autoimmune problems.
CORTICOSTEROIDS
Excellent for use in the short term to manage site-specific relief for aggravated inflammation in a particular joint. As a powerful anti-inflammatory, corticosteroid injections can be administered directly into the affected joint or tendon. The drug can also be given as an IM injection in a slow-release form. As there are some potential side-effects in using corticosteroids, their use is usually limited to three times a year, with a three-month gap for repeat use to the same joint. This is because long-term use of even low-dose corticosteroids may result in osteoporosis and other steroid-related side-effects such as weight gain, thinning skin, easy bruising, and high blood pressure.
DMARDS (DISEASE-MODIFYING ANTI-RHEUMATIC DRUGS)
Whilst a commonly-used treatment in other forms of arthritis, their use in the treatment of AS is limited, as their benefits do not extend to the spine. Their effect may be beneficial in reducing damage and pain in other joints. Examples of DMARDs include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine, but I will not go into more detail into them in this article due to their limited use in AS.
PHYSIOTHERAPY AND EXERCISE
The efficacy and long-term benefit of any drug treatment can only achieve so much as a stand-alone therapy. Physiotherapy and regular exercise will not only improve and maintain levels of mobility, but also enhance the effectiveness of medication. Building up exercise levels gradually is the key, especially if lifestyle has been fairly sedentary. Doing too much too soon can be harmful and put people off resuming exercise.
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in the successful treatment of AS and combined with a personalised exercise programme, can dramatically slow down the progress of the disease.
Patients should think ‘Keeping moving keeps me moving’. An individual exercise programme designed by the physio will focus on exercises which add strength to affected areas whilst improving mobility in the spine and other affected joints through daily stretching — especially at the start of the day — will add significant benefit to quality of life.
Another important aspect of good physio will be advice and exercises that focus on maintaining good posture during day-to-day activities such as driving, using the computer (especially at work) or daily household chores.
Hydrotherapy — exercising in water, either in a specially-designed pool or bath or just at your local pool, can be of real benefit to those with AS. The buoyancy of the water offers the ability to exercise the whole body in a supported way and makes movement easier and less stressful on the joints. There are many local ‘aqua-therapy’ groups around, specially focused on the management of arthritic conditions.
There are many other therapies which can offer great benefit to maintaining posture and flexibility, such as yoga, Pilates, etc.
If a patient enjoys competitive sport, then the physio can help them explore low-impact options.
It’s important to note here that whilst massage for muscle and tissue can be beneficial, therapies such as osteopathy, chiropractic or anything that manipulates bones, especially in the spine, are not suitable for those with AS.
As part of an overall wellbeing programme, obvious things to consider would be:
- Maintaining a healthy weight — obvious benefits in the reduction of stress on the joints that comes from being overweight or obese.
- Healthy and balanced diet — given the nature of AS, a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D helps maintain bone density and strength.
- Stop smoking — whilst this has obvious numerous health benefits, it is particularly important for those whose lung capacity and breathing has been adversely affect by onset of AS in the thoracic region.
OUTLOOK
As stated earlier, there is no cure for AS. However, for the majority, with early action, the right medication combined with a tailored, daily exercise routine along with a general healthy outlook, those living with AS can do a lot to mitigate the effects of the condition and enjoy a decent quality of life.